Connected vs isolated photovoltaic installations

Claudia Pardo, Content Specialist at Sunhero and a firm believer that solar energy can transform the world.
05/08/2024
3 min read
Table of Contents
Solar energy has established itself as an increasingly attractive energy solution, gaining ground over conventional energy sources.
When planning the installation of a photovoltaic system, it is important to decide between a grid-connected system (on-grid) or an isolated system (off-grid).
In this post, we will explain the main differences between these two systems and we will go into the advantages and disadvantages they offer.
Connected photovoltaic installation
A grid-connected PV system, also known as “on-grid”, means that the system is linked directly to the electricity grid.
This configuration allows owners to consume electricity generated by the solar panels and sell surplus energy to the grid.
The grid-connected photovoltaic system has specific characteristics, some of which are considered advantages and others are considered disadvantages. Below, we review some of them:
Advantages
Lower initial investment: As this system does not require storage batteries, the installation costs are significantly lower. This reduction in initial costs allows the system to be amortised more easily, making investment in solar energy more accessible and profitable in the short term.
Selling Surplus: Users can sell excess energy generated by their solar panels to the grid through net balancing. When solar panels produce more electricity than is consumed, the excess is sent to the grid and recorded as a credit. This credit offsets the cost of electricity consumed when the panels do not generate enough power, such as at night or on cloudy days. Over time, these credits can accumulate and fully cover the electricity consumption, resulting in a zero bill.
Reliability: An on-grid PV system is highly reliable, as the grid acts as a backup when the solar panels do not generate enough power, such as at night or on cloudy days. This ensures a constant supply of electricity as you will always have access to the power you need.
Disadvantages
Grid dependency: If there is a power outage in the grid, the system will stop working, as it depends on the grid to operate. During blackouts, there will be no power supply, even if the solar panels are generating power. This can be solved with a storage battery, which allows the energy generated by the solar panels to continue to be used.
Isolated photovoltaic installation
On the other hand, an off-grid installation is not connected to the grid and relies entirely on the energy generated by the solar panels.
This type of system requires batteries to store the energy.
Advantages
Energy Independence: Users are completely independent from the grid and are not affected by power outages. This means that they can access a constant power supply without worrying about grid interruptions.
Remote locations: This system is ideal for rural or more isolated areas where there is no access to the grid. In these regions, installing an off-grid PV system may be the only viable option for obtaining electricity.
Disadvantages
High initial investment: The need for batteries and other storage components increases initial costs. These systems require higher investment in advanced technology and additional equipment, which can make the initial installation considerably more expensive compared to grid-connected systems.
Battery maintenance: Batteries require regular maintenance and have a limited lifespan, which means periodic replacements. Proper battery care is essential to ensure efficient operation and prolong battery life, but this entails additional effort and ongoing costs.
Power limitation: During prolonged periods of bad weather or high demand, there may be limitations on power availability. Off-grid PV systems rely solely on solar energy and battery storage capacity, which may be insufficient in adverse conditions or during high peak consumption.
How does a photovoltaic system work?
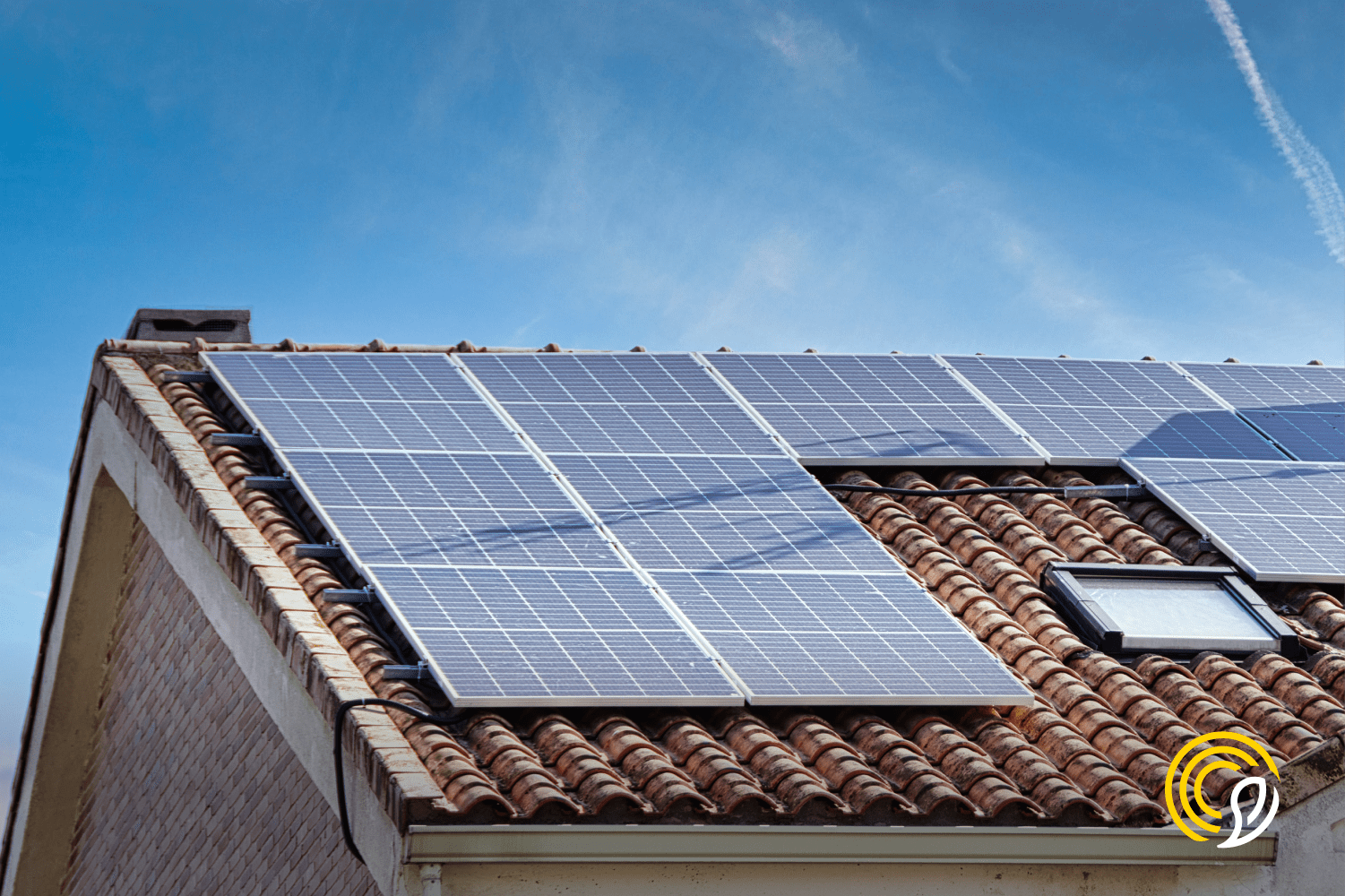
A typical PV system includes solar panels, an inverter, a mounting system and, in the case of off-grid systems, batteries. The solar panels capture sunlight and, through the photovoltaic effect, convert solar energy into electricity. The inverter converts this electricity from direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC), which is the form of electricity used in most homes and businesses.
In short, the choice between grid-connected and off-grid photovoltaic installations will depend on factors such as location, budget and the specific energy needs of each user.
If you want to know which installation is the most suitable for you, write to us and our experts will give you personalised advice, free of charge and without obligation.
Start today!
Fill out our free solar calculator and get a custom quotation