How much energy does a solar panel produce?

Claudia Pardo, Content Specialist at Sunhero and a firm believer that solar energy can transform the world.
08/11/2024
4 min read
Table of Contents
If you’re thinking about switching to solar energy and installing solar panels at home, you’ve likely wondered: How much electricity can a solar panel really generate? This figure is more than just a number; it’s the key to understanding how much you can reduce your electricity consumption and, ultimately, how much you could save on your bill.
In this article, we’ll explain how solar panel energy production is measured, what factors affect its performance, and how you can estimate electricity generation under real-world conditions. Additionally, we’ll offer some tips to optimize your solar installation and make the most of every ray of sunlight in your location.
What is the power of a standard solar panel?
Solar panels come in various sizes and capacities to meet different household needs. For a residential installation, a 400W panel is a common choice and a good starting point for those looking to generate their own energy.
This 400W power rating means that, under ideal conditions, the panel can produce up to 400 watt-hours in one hour of direct sunlight. However, in practice, daily production depends on factors like the hours of direct sunlight the panel receives and its orientation.
Solar panel performance
Another important factor to consider is the performance of a solar panel, which is its ability to efficiently convert sunlight into electricity.
To evaluate a solar panel’s performance, manufacturers typically conduct two types of tests. The first is performed under Standard Test Conditions (STC), which simulate a day with ideal light and temperature (25ºC). In this test, a 400W panel should generate its maximum output, expressed as “watt peak” (Wp).
For a more realistic estimate, a second test called NOCT (Normal Operating Cell Temperature) is used. This test measures energy output under more typical conditions, such as a temperature of 20ºC and lower solar radiation.
This second data point serves as a useful reference for understanding how much the panel will produce under more everyday conditions. According to PV Magazine, NOCT values give consumers more realistic expectations of energy output when purchasing a solar panel.
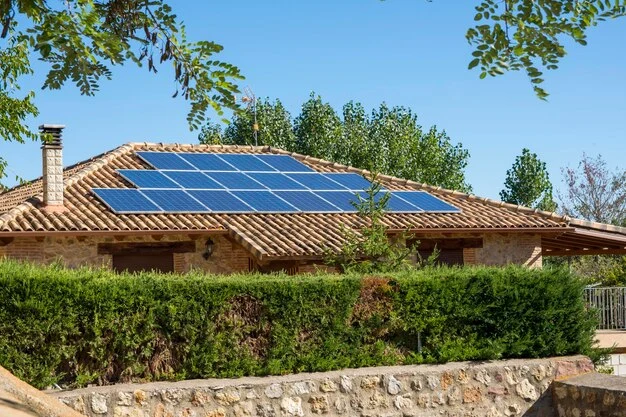

How much energy can a 400W solar panel generate?
According to the Institute for Energy Diversification and Saving (IDAE), a 400W panel can generate around 2 kWh per day on average, provided it receives approximately five hours of direct sunlight each day. This calculation is based on Standard Test Conditions (STC), which simulate an ideal scenario with specific light and temperature conditions (25ºC) and a solar intensity of 1000W/m².
In other words, on a day with these ideal conditions, a 400W panel would produce 400 watt-hours per hour of direct sunlight. Thus, with five hours of sunlight, the panel would achieve a total of 2 kWh per day (400W x 5 hours = 2000 Wh or 2 kWh). However, it’s important to remember that this is an estimate, and actual output may vary depending on factors such as geographic location, panel tilt and orientation, and weather conditions.
To help you more accurately calculate how much energy you can generate and save at home, visit our solar calculator.
Factors affecting solar panel energy production
Several factors influence the amount of electricity a solar panel can produce:
- Daily Sunlight Hours: The amount of sunlight a specific region receives directly affects the energy a panel can produce. Sunlight hours are determined by the latitude and climate of the region. In Spain, for instance, sunlight hours vary from north to south. According to the IDAE, cities like Málaga receive more annual sunlight hours, increasing the potential energy output compared to cities like San Sebastián.
- Orientation and Tilt: The panel’s direction and angle are crucial for capturing the maximum amount of sunlight. In the Northern Hemisphere, panels are generally oriented south to maximize sunlight exposure, and the ideal tilt varies depending on the latitude. In Spain, a tilt between 20° and 40° is usually adequate, although small adjustments can further optimize production depending on the season.
- Panel Efficiency: Not all solar panels are equally efficient. Monocrystalline panels tend to be more efficient than polycrystalline ones due to their structure, and the purity of the silicon used also plays a role. Additionally, larger panels, though requiring more space, generate more energy, making them ideal for those looking to maximize production.
Tips to optimize your solar panel production
To make the most of your solar installation, here are some useful tips:
- Proper Orientation and Tilt: Adjusting the panel’s orientation and tilt is essential for maximizing sunlight capture. In the Northern Hemisphere, orienting them south and adjusting the tilt according to local latitude significantly boosts production.
- Regular Maintenance: Solar panels need to stay free from dust, dirt, and debris to perform at their best. Regular cleaning and maintenance are crucial to prevent efficiency loss.
- Shade Optimization: Avoiding shadows on the panels is essential, as even small obstructions can greatly reduce energy output. If unavoidable shading exists, microinverters or power optimizers can be installed to mitigate the loss.
With these recommendations and a well-planned installation, you can ensure that your photovoltaic system operates optimally, making the most of every ray of sunlight. At Sunhero, we analyze each client’s needs individually, ensuring we provide a system tailored to their consumption and location for maximum efficiency and performance guarantees in solar energy production.
Start today!
Fill out our free solar calculator and get a custom quotation