What is the photovoltaic effect?

Head of Sales Operations and Marketing at Sunhero, specialised in strategic planning and commercial excellence, passionately advancing solar energy adoption across Spain.
15/11/2024
4 min read
Table of Contents
Solar energy is a type of renewable energy considered clean, free, and inexhaustible. It can be harnessed in various ways, such as generating electrical energy. Typically, this type of energy is produced through the installation of solar panels. Although most solar panel users know that this generates solar energy, they often cannot fully explain how. In reality, it is thanks to what is called the photovoltaic effect. Here we will explain what it is and how it works.
What is the photovoltaic effect?
The photovoltaic effect is a photoelectric reaction that occurs between two different materials when exposed to electromagnetic radiation, i.e., sunlight, generating an electric current.
In solar panels, the photovoltaic effect occurs between two pieces of silicon, the semiconductor material from which photovoltaic cells are made. The function of each of these cells is to absorb solar radiation.
When this happens, electrons move from one semiconductor layer to another within the solar cell, creating an electrical current. This movement is facilitated by the photovoltaic effect, which is triggered when the sun’s photons impact and energize an electron in the silicon, initiating the effect.
What are photons?
A crucial element in the process of generating electricity is the photon, a particle emitted from solar radiation. When a photon alters an electron in the silicon, the photovoltaic effect occurs.
Thus, it can be said that the photon is responsible for initiating the production of electrical current by transferring its energy to the electrons.
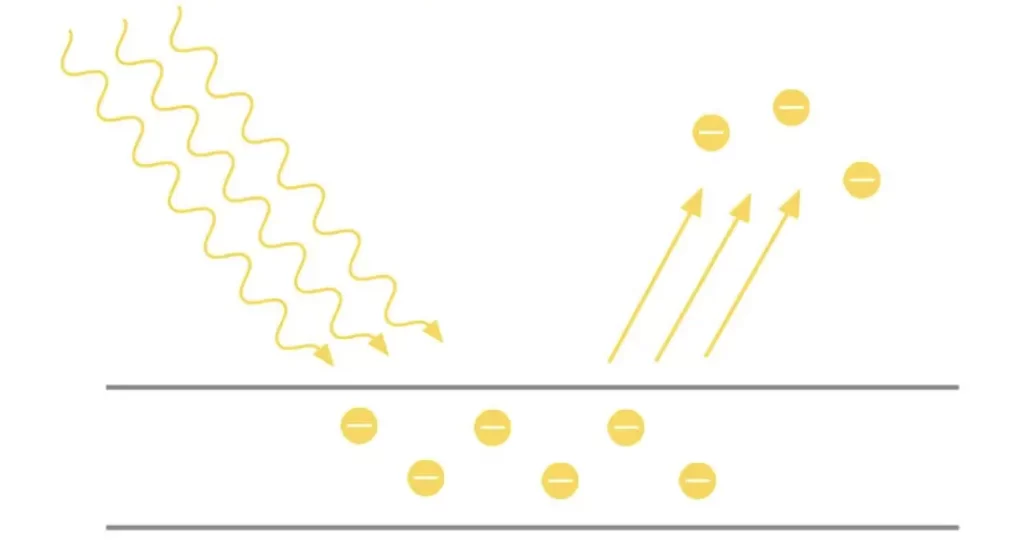
This process does not occur with all photons, only with those capable of consistently altering the electrons to turn the silicon from which the photovoltaic cells are made into conductive material.
Thanks to the silicon becoming a conductive material, the continuous energy can travel through the panel to the inverter, which converts the direct current into alternating current. This converted energy can then be used not only in homes but also in commercial and industrial settings, powering everything from office buildings to manufacturing facilities.
Why do not all light particles convert into electrical energy?
As mentioned earlier, the process by which a photon alters the electrons is not perfect and consequently has energy losses. This is not because the photons are not capable of providing enough energy to cause the necessary movement of electrons, but because some photons lose part of their momentum as they pass through the silicon in the solar cells. These losses, inherent to the interaction between light and the silicon, are inevitable, although manufacturers are working hard to minimise these losses.
Specifically, the photovoltaic effect is achieved as long as the energy of the incident photon—the light particle hitting the solar cell—is greater than 1.2 electron volts (eV). This threshold is crucial because it represents the minimum amount of energy needed to dislodge an electron within the silicon, allowing it to move freely and create an electrical current.
Differences between the photoelectric effect and the photovoltaic effect
The photoelectriceffect is the process by which electrons are released from a material due to the action of electromagnetic radiation. That is, the photoelectric effect is responsible for the production of free electrons, while the photovoltaic effect is the subsequent process by which electrical current is produced thanks to those free electrons we mentioned.
The photoelectriceffect involves the emission of electrons from a material, such as the silicon used in solar cells, due to the absorption of photons (this is dependent on the frequency of light). Conversely, the photovoltaic effect is the generation of electrical current in a semiconductor material, typically silicon, when it is illuminated (this depends on the intensity of light).
How is the electrical current generated in a solar panel?
After this explanation, we delve into how the electrical current is generated. Each electron that is freed leaves behind a hole, or free space, that is then occupied by another electron that has jumped from another atom.
These movements of electrons released from the spaces they leave behind are known as electrical current.
Certainly, these issues are very technical and form part of the knowledge of how a solar panel works as a whole. Remember, however, that the solar panel is just one of the two essential elements that make up a photovoltaic installation. Without the inverter, a home could not use the energy generated by the panel, since it is this element that is responsible for transforming the direct current produced into alternating current, which is used by the electronic devices in a home.
At Sunhero, we not only take care of installing high-quality solar panels, but we also ensure that the entire process of conversion and utilisation of solar energy is efficient and reliable. Use our solar calculator and find out how much energy you can generate with solar panels.
FAQ
What is the photovoltaic effect?
The photovoltaic effect is the generation of electric current in a solar cell when it is exposed to sunlight, due to the interaction of photons with electrons in the semiconductor material.
How does the photovoltaic effect differ from the photoelectric effect?
The photoelectric effect involves the emission of electrons due to light absorption, affecting the frequency of light, while the photovoltaic effect involves generating electrical current due to light intensity.
What role do photons play in the photovoltaic effect?
Photons are responsible for initiating the production of electrical current by imparting their energy to the electrons in the solar cell material.
Why does not every photon contribute to electricity generation?
Not every photon has enough energy to consistently alter electrons to create a conductive state in the silicon; some energy is inevitably lost in the material.
What is necessary for a home to use the energy produced by solar panels?
An inverter is essential for converting the direct current generated by solar panels into alternating current that can be used by home appliances.
Start today!
Fill out our free solar calculator and get a custom quotation