Renewable Energies – Types and Characteristics

Claudia Pardo, Content Specialist at Sunhero and a firm believer that solar energy can transform the world.
17/12/2023
5 min read
Table of Contents
Renewable energy refers to energy sources that are obtained from inexhaustible natural resources. Today, they represent the sustainable alternative to conventional energy sources such as coal, oil or fossil fuels.
In the following article, we will explain what types of renewable energies exist, what are the main characteristics, the most important advantages and disadvantages of each of them.
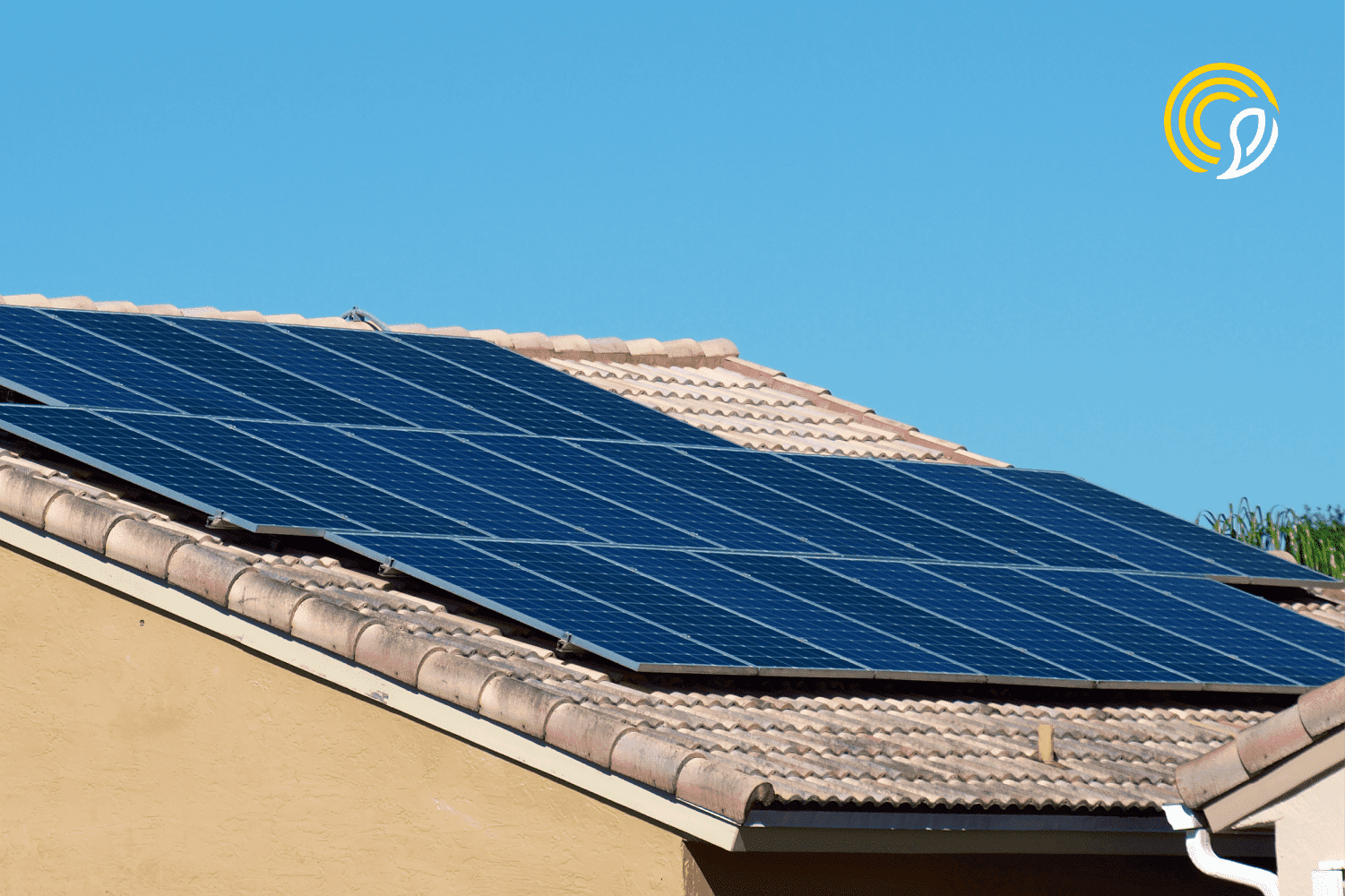
Solar energy
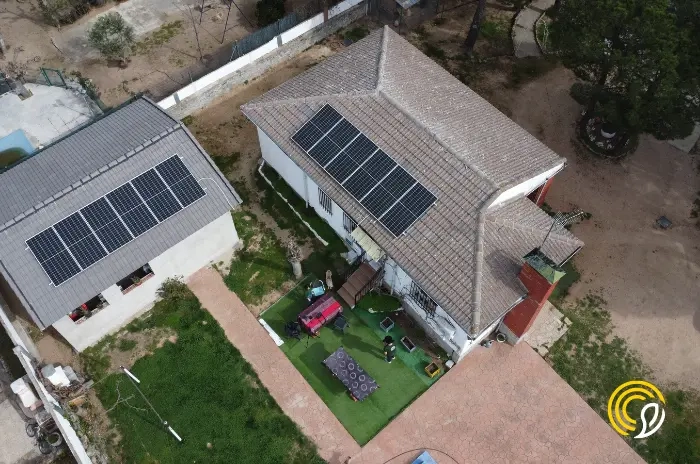
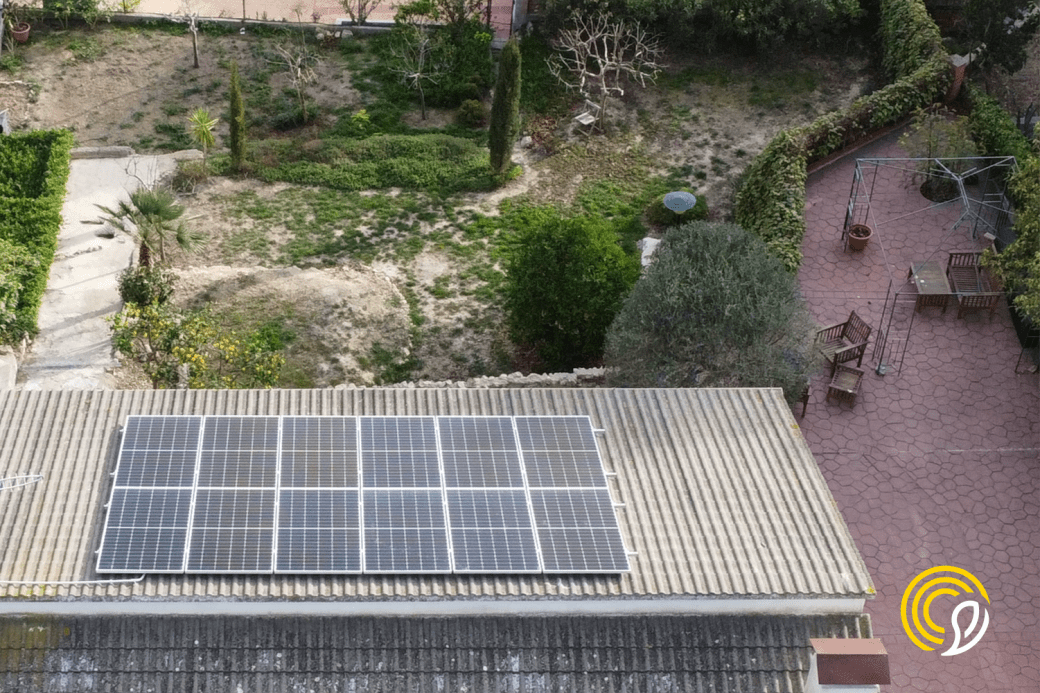
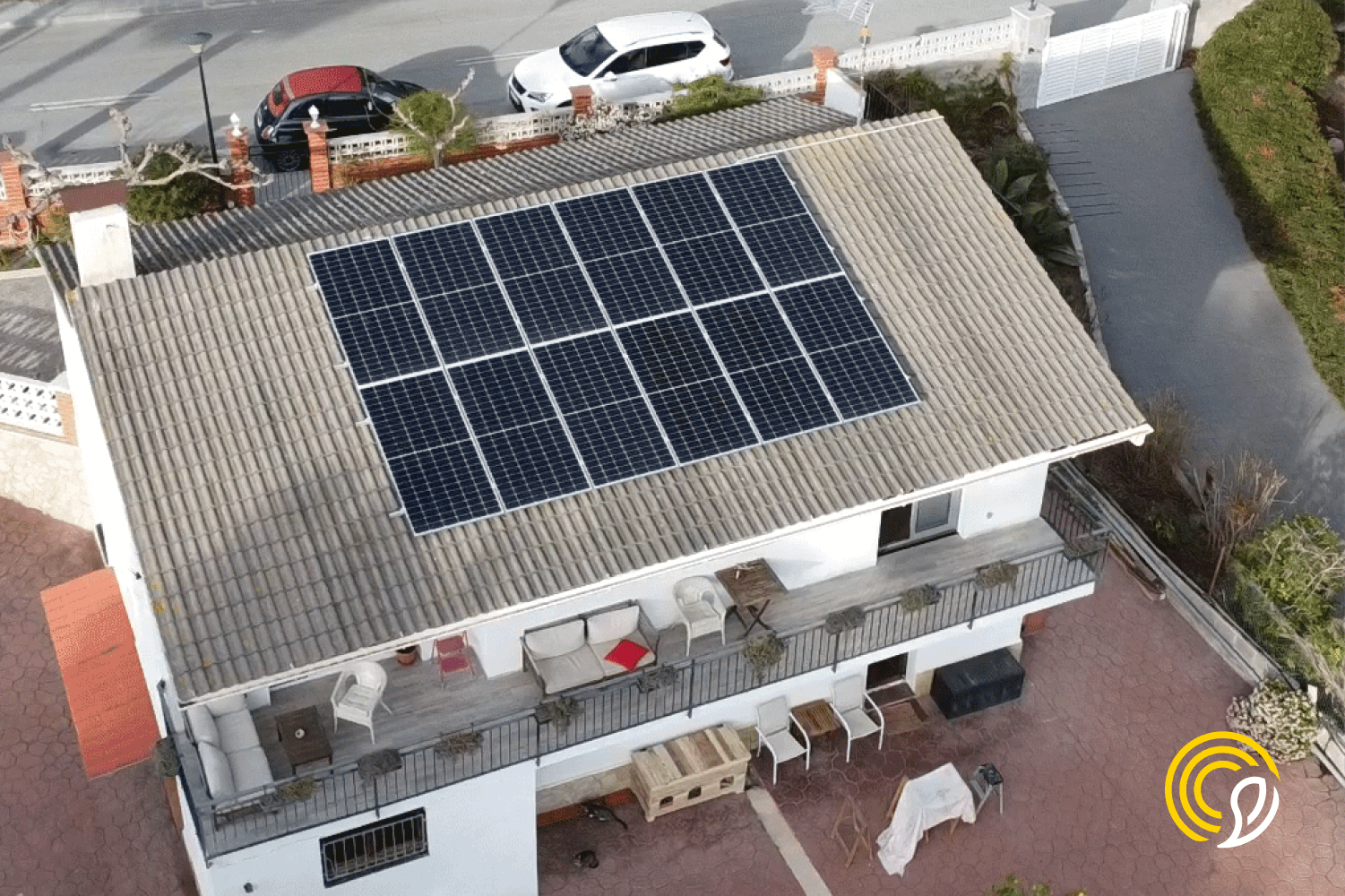
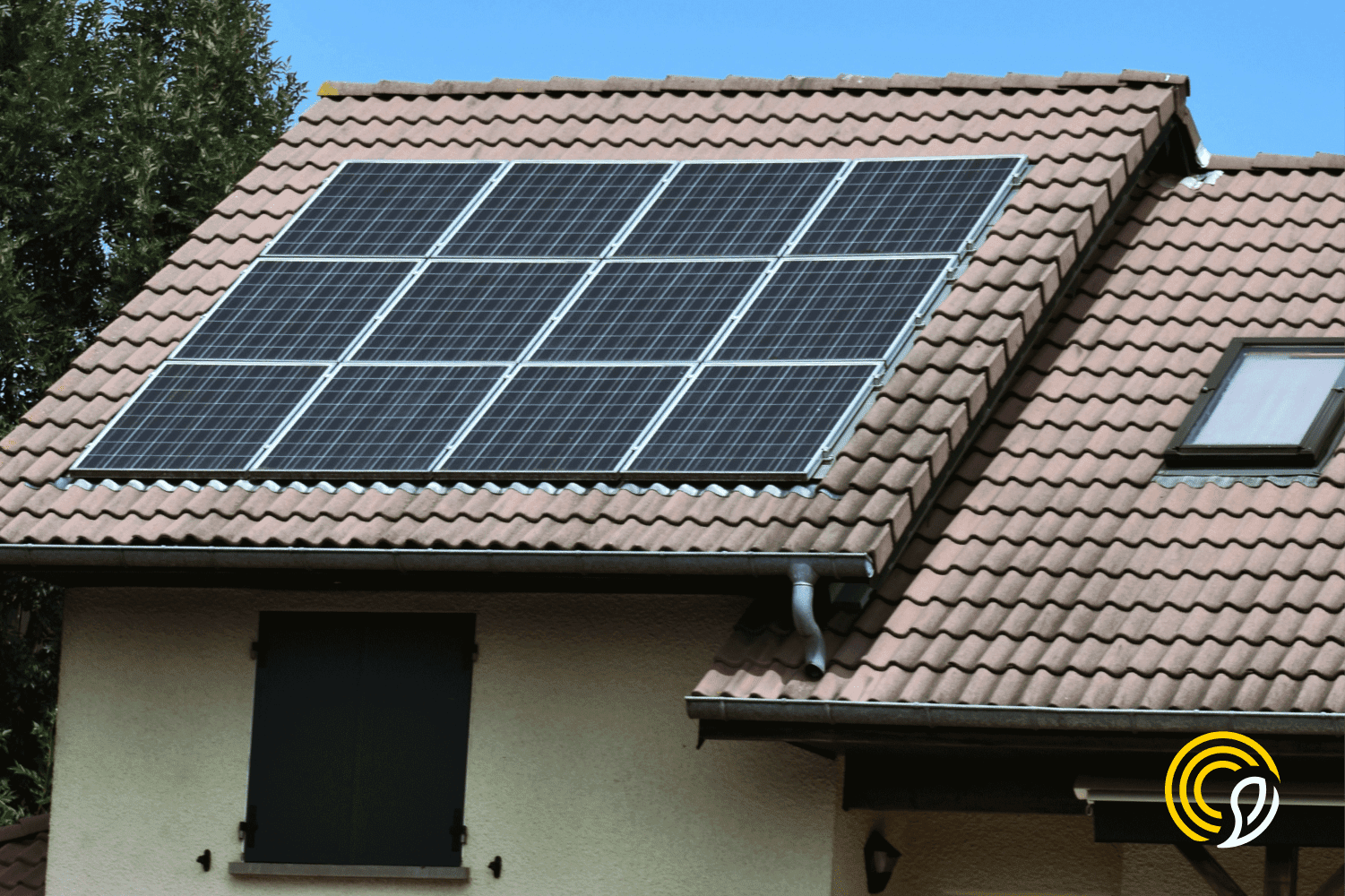
Solar energy, as its name suggests, comes from the sun. This energy is captured by solar panels, which absorb solar radiation and convert it into electricity. This generated electricity can be stored for later use or fed directly into the electricity grid.
In addition to photovoltaic solar energy, there is another type of solar energy, solar thermal energy. In this case, the sun’s energy is used to heat a liquid, usually water, until it turns into steam. This steam then drives a turbine, generating electricity.
Advantages
- It is a clean and sustainable energy that does not generate greenhouse gases and helps to significantly reduce the carbon footprint.
- Solar radiation is very abundant and solar panels can be used in remote places where the traditional electricity grid does not reach.
- Producing solar energy with solar panels reduces electricity bills and allows for greater energy independence from large electricity companies.
- Once the photovoltaic system is installed, solar panels require little maintenance and have a useful life of about 25 years, making them a profitable long-term investment.
Disadvantages
- Solar energy requires a high initial investment, although nowadays there are subsidies and grants available and the photovoltaic system pays for itself within a few years.
- Solar energy is not constant and is only generated during the day by solar radiation.
- The efficiency of solar panels is related to sunlight, so on rainy or cloudy days, they can produce less energy.
- Photovoltaics require a large amount of space to be efficient, which can be a problem for use in large cities or small spaces.
Wind energy
Wind energy is a form of renewable energy that uses the power of the wind to generate electricity. This type of energy is produced by wind turbines that convert the kinetic energy, produced by wind currents, into electrical energy.
Like solar energy, wind energy can be used on a large scale, in large wind farms, but also in residential and small businesses.
Advantages
- Wind energy is a renewable and sustainable source. Because it comes from the wind, it is an inexhaustible source of energy.
- Wind energy requires little space. In fact, with less space than photovoltaics, it produces and stores the same amount of energy.
- Maintenance is relatively low. Wind energy installations operate with turbines, which do not require fuel and have few moving parts, reducing the need for repairs.
- Wind energy is highly scalable, it can be adapted to different needs and geographical contexts.
Disadvantages
- Wind energy is intermittent, as it depends on the wind and can vary in intensity, meaning that energy production does not always coincide with demand.
- The initial investment is high. To produce wind energy requires the installation of wind turbines, infrastructure and connection to the electricity grid.
- Wind turbines can have a negative impact on the landscape, especially in rural or natural areas. In addition, they can produce a level of noise that can be disturbing for neighbours living nearby.
Hydropower
Hydropower or hydroelectric power is a form of renewable energy that uses the movement of water, such as the flow of rivers, waterfalls or tides to generate electricity. This form of energy production has one of the longest traditions and represents one of the oldest renewable energy sources.
There are different types of hydroelectric power plants, depending on type and size. On the one hand, there are reservoir power plants, which store and release water according to the demand for energy. On the other hand, there are pumped-storage power plants, which store energy by pumping water to a higher level and generate electricity when it is released. In addition, there are also mini-hydro plants for small-scale power generation in rural or remote areas.
Advantages
- It is a renewable and sustainable energy, as it is based on the water cycle, a natural and renewable source, to produce energy.
- Hydropower plants generate very low greenhouse gas emissions, especially when compared to fossil fuel power sources.
- It is one of the most efficient renewable energy sources, converting approximately 90% of the potential energy of water into electricity.
- Hydroelectric power plants with reservoirs can store energy, which means that production can be adjusted according to demand.
Disadvantages
- The construction of large dams can have a negative impact on ecosystems. This includes the alteration of aquatic and terrestrial habitats, affecting flora and fauna.
- The construction of hydropower plants involves a very high initial investment and can take a long time, which delays the return on investment.
- Changes in rainfall patterns and river flows can affect the availability of water for hydropower generation.
- Water temperature and quality can be altered, affecting aquatic life and possibly reducing the water’s suitability for certain uses.
Geothermal energy
Geothermal energy is a renewable energy source that harnesses heat from within the earth. In order to obtain this type of energy, it is necessary to drill into the earth’s surface to access underground steam and hot water, which are then used to drive turbines and generate electricity or direct heating.
Advantages
- Geothermal energy, unlike wind and solar energy, is a continuous form of energy, as it does not depend on weather conditions.
- Geothermal power plants offer high efficiency in the conversion of heat into electrical energy.
- Geothermal energy provides great versatility, as it can be used to generate electricity but also for direct heating and cooling.
Disadvantages
- Geothermal energy, because it relies on underground heat sources, limits its development to specific areas with significant geothermal activity, such as volcanic regions, for example.
- It can lead to local impacts such as groundwater contamination or land disturbance if proper practices are not followed.
- The construction of geothermal plants involves a large initial investment due to the infrastructure required for their development.
Biomass
Biomass is a renewable energy source that produces heat or electricity from organic matter such as wood, municipal waste, agricultural waste or animal manure.
Energy conversion is achieved through direct combustion, gasification, fermentation and anaerobic digestion. These processes transform biomass into energy.
Advantages
- Biomass contributes to the reduction of organic wasteand residues by converting them into energy. This reduces the need for landfill.
- It is compatible with existing systems with minimal adaptations, e.g. in coal-fired power plants.
- In addition to being a renewable energy source, the use of biomass can also produce other products such as building materials or biofertilisers.
Disadvantages
- During the biomass combustion process, pollutant gases such as carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides may be released.
- Energy produced from biomass can be more expensivethan from other renewable sources due to the collection, processing and transportation process required.
- The availability of biomass is subject to external factors, such as seasonality and climatic conditions.
Ocean energy
Ocean energy, also known as ocean energy, is a form of renewable energy that is derived from the energy potential of the oceans. It is an energy that, compared to other renewable energy sources such as wind or solar, is still in the early stages of development.
Within ocean energy, we can find different categories, such as tidal energy, wave energy, ocean thermal energy or ocean current energy.
Advantages
- Tidal energy and some forms of wave energy are more predictable than solar and wind energy. For this reason, it is easier to plan for their generation.
- Seventy percent of the earth’s surface is covered by the oceans, which represents a very large potential for the implementation of ocean energy technology.
- Ocean energy installations have a very low visual impact and generally require less space than other renewable energy sources.
Disadvantages
- This type of renewable energy may require higher maintenance and may even affect the durability and lifetime of the installations, as the marine environment is corrosive.
- The technology to harness ocean energy is still under development, which implies higher upfront costs for research and implementation.
- Ecosystems and marine life can be affected by such energy installations, as well as altering sedimentation patterns and local currents.
Start today!
Fill out our free solar calculator and get a custom quotation